
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is a part of the nervous system that consists of nerves and ganglia located outside of the brain and spinal cord. It is responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system (CNS) and the rest of the body, including muscles, organs, and tissues. The PNS includes sensory nerves that convey information from the body to the CNS and motor nerves that carry signals from the CNS to muscles and organs, allowing for voluntary and involuntary movement.
Peripheral neuropathy refers to a condition in which there is damage to the peripheral nerves, disrupting their normal functioning. It can affect multiple nerves in different areas of the body simultaneously (polyneuropathy) or a single nerve (mononeuropathy). Peripheral neuropathy can result from various causes, including physical injury, infections, metabolic disorders, autoimmune diseases, toxic exposure, and certain medications. These various causes result in a reduction of blood flow (microcirculation) to the nerves. The nerves do not receive the appropriate oxygen and nutrients from the blood resulting in nerve damage, and for most patients, it results in pain and lifestyle modifications.
FREE Nerve Scan
We’ll use two tests to evaluate blood flow and sensory nerve damage in your feet and hands.
- Thermal Imaging – assesses changes in blood flow. Decreased blood flow means less oxygen and nutrients and decreased circulation.
- Electrical Conductivity Gloves – assess sensory nerve damage in the feet and hands.
The results of the two tests will either qualify or disqualify you for more advanced nerve testing with the doctor.
How Our Neuropathy Relief Plan Works
Real answers and real solutions to solving your neuropathy
1. Schedule Your Free Nerve Scan
The free nerve scan will assess both blood flow and nerve sensitivity. The outcome of these tests will help determine if you qualify for an advanced sensory examination with the doctor.
2. Be Truly Heard and Understood
We will take the time to truly listen to your unique situation. We want to know how neuropathy is affecting your life, the therapies you have tried, and your health goals.
3. Get a Personalized Plan of Action
A custom plan of attack is designed around your life to help rebuild your nerves, decrease pain levels, and improve your balance. This will help to get you back to the life you deserve.
Neuropathy Symptoms
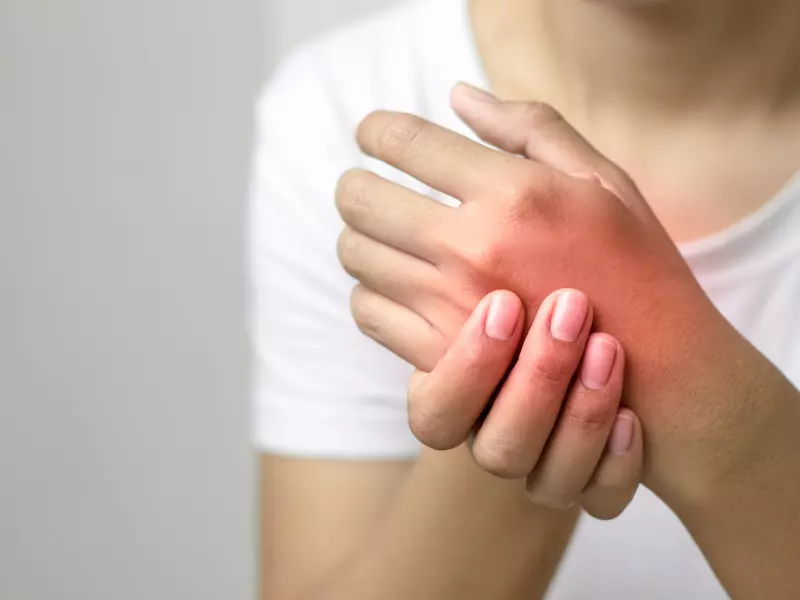
Neuropathy, or peripheral neuropathy, occurs when there is damage or dysfunction to the peripheral nerves. This damage disrupts the normal functioning of the nerves and impairs their ability to transmit signals effectively. The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy can vary depending on the type of nerves affected (sensory, motor, or autonomic) and the underlying cause of the neuropathy. Here are some common symptoms associated with peripheral neuropathy:
The three types of neuropathy can affect the PNS in several ways:
Sensory Neuropathy – affects nerves that control sensation, symptoms include:
- Tingling or “pins and needles” sensation in the hands, feet, or other affected areas
- Numbness or reduced sensation in the hands, feet, or other areas of the body
- Burning or shooting pain, which may be constant or intermittent
- Hypersensitivity to touch or temperature changes
- Loss of coordination or difficulty with fine motor skills
Motor Neuropathy – affects motor nerves, symptoms include:
- Muscle weakness, especially in the hands or feet
- Muscle cramps or muscle twitching
- Difficulty with balance and coordination
- Changes in gait or walking pattern
- Muscle wasting or decreased muscle mass
Autonomic Neuropathy – affects the autonomic nerves, which control involuntary functions of the body, symptoms include:
- Abnormal blood pressure or heart rate, such as orthostatic hypotension (a drop in blood pressure upon standing up) or tachycardia (rapid heart rate)
- Digestive problems, including nausea, vomiting, bloating, diarrhea, or constipation
- Bladder dysfunction, such as urinary urgency, frequency, or incontinence
- Sexual dysfunction, including erectile dysfunction in men or decreased libido in both men and women
- Sweating abnormalities, such as excessive sweating or lack of sweating
It’s important to note that not all individuals with peripheral neuropathy experience the same combination or severity of symptoms. The symptoms can progress gradually over time or appear suddenly and progress rapidly.
If you suspect you have peripheral neuropathy or are experiencing symptoms, we recommend you take advantage of our free nerve damage screening. The free nerve damage screening will assess blood flow and sensation and help the staff determine if you are a good candidate for an advanced examination with the doctor.
Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
A wide range of factors can cause peripheral neuropathy. Some of the common causes include:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels over an extended period can damage nerves, leading to neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy is a prevalent form of peripheral neuropathy.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical injuries, such as a car accident, fall, or sports injury, can damage peripheral nerves and result in neuropathy.
- Infections: Certain infections, including shingles (herpes zoster), Lyme disease, HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C, and Epstein-Barr virus, can cause peripheral neuropathy.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) involve the immune system attacking the nerves.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins B1 (thiamine), B6, B12, and E, as well as niacin and folate, can contribute to peripheral neuropathy.
- Alcohol Abuse: Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption can cause nerve damage and peripheral neuropathy.
- Medications and Toxins: Certain medications can lead to neuropathy, including chemotherapy drugs, antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV, and antibiotics.Exposure to toxins like heavy metals (lead, mercury), industrial chemicals, and pesticides can also cause nerve damage.
- Genetic Factors: Some inherited disorders, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, can result in peripheral neuropathy.
- Kidney or Liver Disorders: Conditions affecting the kidneys or liver can cause an imbalance of chemicals and toxins in the body, leading to nerve damage.
- Other Medical Conditions: Peripheral neuropathy can be associated with hypothyroidism, cancer, multiple sclerosis, amyloidosis, and more.
It’s important to note that these are just some common causes, and there may be other less common or unknown causes of peripheral neuropathy. The providers and staff at North Idaho Neuropathy can conduct a thorough examination, review your history, and set an appropriate treatment plan to help you stop this condition and regain your quality of life.
Peripheral neuropathy is a common condition that affects a significant number of people worldwide. However, it is challenging to provide an exact number as the prevalence can vary depending on the population studied and the underlying causes. Here are some general statistics:
- United States: It is estimated that peripheral neuropathy affects approximately 20 million people, making it widespread.
- Global Estimates: Globally, it is difficult to determine the exact prevalence of peripheral neuropathy due to variations in reporting and diagnosis. However, it is believed to affect millions of individuals worldwide.
- Diabetes-Related Neuropathy: Among individuals with diabetes, it is estimated that up to 50% may develop peripheral neuropathy at some point in their lives. Given the increasing prevalence of diabetes globally, this contributes significantly to the overall number of people affected by neuropathy.
- Age-Related Neuropathy: Peripheral neuropathy becomes more common with age. Studies have suggested that up to 30% of individuals over 65 may have some form of neuropathy.
Other underlying conditions, such as autoimmune disorders, infections, and certain medications, can also contribute to the development of peripheral neuropathy.
It’s important to note that peripheral neuropathy can vary in severity and presentation. Some individuals may experience mild symptoms that do not significantly impact their daily lives, while others may have more severe symptoms that affect their mobility and overall quality of life.
Conventional Neuropathy Treatment
The conventional medical treatment for peripheral neuropathy is pain management. Here are some commonly used treatment approaches:
- Medications: Certain medications can mask the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. These may include pain relievers such as over-the-counter painkillers (e.g., acetaminophen), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and prescription medications like gabapentin or pregabalin, which have extreme side effects. In some cases, antidepressants or anticonvulsant medications may be prescribed to alleviate nerve pain.
- Topical treatments: Creams, gels, or patches containing medications such as lidocaine can be applied to the skin to provide localized pain relief.
- Physical therapy: It involves exercises and techniques to improve strength, balance, coordination, and mobility, which may help manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle modifications: Certain lifestyle changes can help manage peripheral neuropathy symptoms. This may include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and taking steps to prevent injuries or falls.
These conventional medical treatments do not target the root cause or specifically address nerve damage. Most patients with this condition managed with conventional medical treatments are seeing the condition progressively worsen and decreasing quality of life. If you have or suspect you have peripheral neuropathy and are tired of the conventional medical approach to this condition, we recommend you take advantage of our free nerve damage screening. The free nerve damage screening will assess blood flow and sensation and help the staff determine if you are a good candidate for an advanced examination with one of our providers. During the examination and report findings, we will provide recommendations for your specific condition and show you how we naturally treat this condition at the root cause.
Chiropractic Care for Neuropathy Relief
The chiropractic approach to peripheral neuropathy differs from conventional medical treatment in that it focuses on the alignment and function of the spine and nervous system. Misalignments or subluxations in the spine can disrupt the normal flow of nerve impulses and contribute to various health conditions, including neuropathy. Chiropractic treatment aims to correct these misalignments and restore proper nerve function.
Our providers use a variety of techniques to address peripheral neuropathy, including:
- Spinal Adjustments: Our chiropractic providers perform manual adjustments or use specialized instruments to apply controlled force to specific areas of the spine. The goal is to realign the vertebrae and relieve pressure on the nerves.
- Spinal Decompression Therapy: This technique gently stretches the spine to relieve pressure on compressed nerves and promote healing.
- Soft Tissue Therapy: We use the latest advanced therapies to improve circulation, which can help alleviate neuropathic symptoms.
- Nutritional Counseling: Our chiropractors provide guidance on dietary changes and nutritional supplements that can support nerve health and reduce inflammation.
During your examination process, our providers will determine if chiropractic care is necessary for your specific type of peripheral neuropathy. Combining chiropractic care with our advanced home protocol and in-clinic therapies has provided excellent outcomes for our patients.
Check Out Our Post Falls Location
151 West 3rd, Suite 101 Post Falls, ID 83854
How We Treat Peripheral Neuropathy In Post Falls, Idaho
Comprehensive Consultation and Exam
At North Idaho Neuropathy, we prioritize your individual experience during our comprehensive examination process. Our foremost aim is to truly understand how neuropathy impacts your life, your previous attempts at finding relief, and your health objectives. To accurately assess whether peripheral neuropathy is present and its stage, we employ a thorough evaluation that includes a 21-point sensory examination and orthopedic motor tests. Through this examination, we can identify the underlying cause and determine if you qualify for enrollment in our neuropathy program.
Upon confirming that we can assist, our dedicated healthcare professionals will craft a personalized treatment plan tailored to address your specific condition. The following day, we will guide you through a detailed discussion on the percentage of nerve damage, prognosis, expectations for care, and outline your unique treatment plan. Our goal is to ensure you are well informed and actively involved in your healing journey.
Infrared Light Therapy
Red/Infrared Light Therapy is a non-invasive treatment that utilizes specific wavelengths of light to promote healing and provide various therapeutic benefits. Here’s an explanation of how it works, the process involved, the sensation you might experience, and its effectiveness:
- Mechanism of Action: Red/Infrared light therapy operates by emitting light in the range of 660 and 810 nanometers. These wavelengths penetrate the skin and are absorbed by the cells, triggering a series of biochemical reactions. The light energy stimulates the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cells, to produce more adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is essential for cellular metabolism and angiogenesis. This increase in ATP production facilitates tissue repair, reduces inflammation, and enhances overall cellular function. These targeted wavelengths also increase angiogenesis which is essential in the regrowth of blood vessels.
- Process: During a red/infrared light therapy session, you’ll typically be positioned comfortably and treated at home. The infrared light-emitting device will be applied to the targeted area. The device emits a focused beam of light onto the skin, delivering therapeutic wavelengths. The duration of each session can vary depending on the condition being treated and the recommendations of the healthcare professional overseeing the treatment.
- Sensation: The treatment itself is generally painless and non-invasive. Most individuals feel a gentle warming sensation as the red/infrared light penetrates the skin. This warmth is well-tolerated and often provides a relaxing experience during therapy. However, individual experiences may vary; some people may not feel any noticeable sensation.
- Effectiveness: Red/infrared light therapy is effective for a range of conditions. The therapy promotes tissue regeneration and accelerates the healing process, making it beneficial for wound healing, musculoskeletal injuries, and various skin conditions. It can also help to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and improve circulation. Additionally, infrared light therapy has been studied for its potential benefits in reducing oxidative stress, stimulating collagen production, and boosting the immune system.
Nerve Re-Education Stimulation Therapy
The nervous system is a complex network of nerves that transmit signals between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body. It is responsible for coordinating and regulating various bodily functions. The nervous system is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which consists of the nerves that extend from the CNS to the limbs and organs.
Peripheral neuropathy refers to a condition in which there is damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves. This can occur due to a variety of factors that reduce microcirculation, including diabetes, infections, autoimmune disorders, traumatic injuries, and certain medications. Peripheral neuropathy can result in symptoms such as pain, tingling, numbness, weakness, and difficulties with coordination.
Nerve re-education stimulation therapy is a form of therapy specifically designed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathy. Its purpose is to help alleviate the symptoms and improve the functioning of the peripheral nerves. The nerve re-education stimulation therapy device uses a combination of electrical stimulation and biofeedback to stimulate the nerves and promote their regeneration.
During nerve re-education stimulation therapy, electrodes are placed in water, typically in the area affected by peripheral neuropathy. The device delivers small electrical impulses to the nerves that mimic the body’s natural nerve signals. These impulses help to reduce pain, improve blood circulation, and facilitate nerve healing.
Nerve re-education stimulation therapy is one of the therapies we use in our protocol to stop and reverse peripheral neuropathy damage. It will be determined by one of our providers at your examination if this therapy is right for you and your peripheral neuropathy.
Nutrition and Supplementation
Diet can play a significant role in the treatment of peripheral neuropathy. While it cannot cure the condition, a well-balanced and nutrient-rich diet can help manage symptoms, promote nerve health, and support overall well-being. The following recommendations may be helpful:
- Balanced Diet: A diet that includes a variety of anti-inflammatory whole foods can provide essential nutrients for nerve health. Focus on consuming a combination of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Antioxidants can help protect nerve cells from damage caused by oxidative stress. Include foods rich in antioxidants such as berries, leafy greens, colorful vegetables (like bell peppers and tomatoes), nuts, and seeds.
- B Vitamins: B vitamins are essential for nerve health and function. Increase your intake of foods rich in B vitamins, such as whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, dark leafy greens, eggs, dairy products, and lean meats.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit individuals with peripheral neuropathy. Sources include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds.
- Magnesium: Magnesium plays a role in nerve function and can help alleviate neuropathy symptoms. Good sources include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains.
- Limit Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates: High blood sugar levels can contribute to nerve damage. Minimize your intake of sugary foods, desserts, sodas, and refined carbohydrates like white bread, white rice, and sugary cereals.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol can worsen neuropathy symptoms. It is best to avoid or limit alcohol consumption.
In addition to dietary adjustments, certain supplements may benefit peripheral neuropathy. However, consulting a healthcare professional before starting new supplements is important. Some commonly recommended supplements for peripheral neuropathy include:
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA): ALA is a potent antioxidant that may help reduce symptoms and improve nerve function.
- B Vitamins: B complex vitamins, particularly B12 and folate, are crucial for nerve health and function.
- Vitamin D: Adequate vitamin D levels are essential for overall health, including nerve function.
- Nitric Oxide (Blood Flow Enhancement): Nitric oxide helps dilate blood vessels, improving blood flow to peripheral nerves. Enhanced blood flow can provide more oxygen and nutrients to damaged nerves, aiding their repair and reducing symptoms.
While diet and supplementation can be helpful, they should not replace medical treatment or professional advice. Working with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized plan that suits your specific needs is essential.
Neuropathy Restoration Plan
We provide a safe, powerful, and all-natural choice for neuropathy sufferers without addictive medications or surgery. We combine the most advanced, cutting-edge, in-clinic, and home treatments to help resolve your neuropathy condition.
Our exclusive neuropathy relief system increases blood flow to the nerves and re-educates the damaged nerves in the feet and hands, which helps to rejuvenate nerves naturally.
Our Neuropathy Restoration Plan has three main goals:
- Enhance the environment within the body for nerve healing using food as medicine.
- Increase blood flow to the nerves through microcirculation improvement.
- Stimulate the damaged nerves (small fiber, large diameter, or motor nerves) to reduce pain and improve balance.
The amount of treatment needed to allow the nerves to recover varies from person to person and can only be determined after a detailed neurological and vascular evaluation. Your neuropathy may be reversible. We are here to help.

